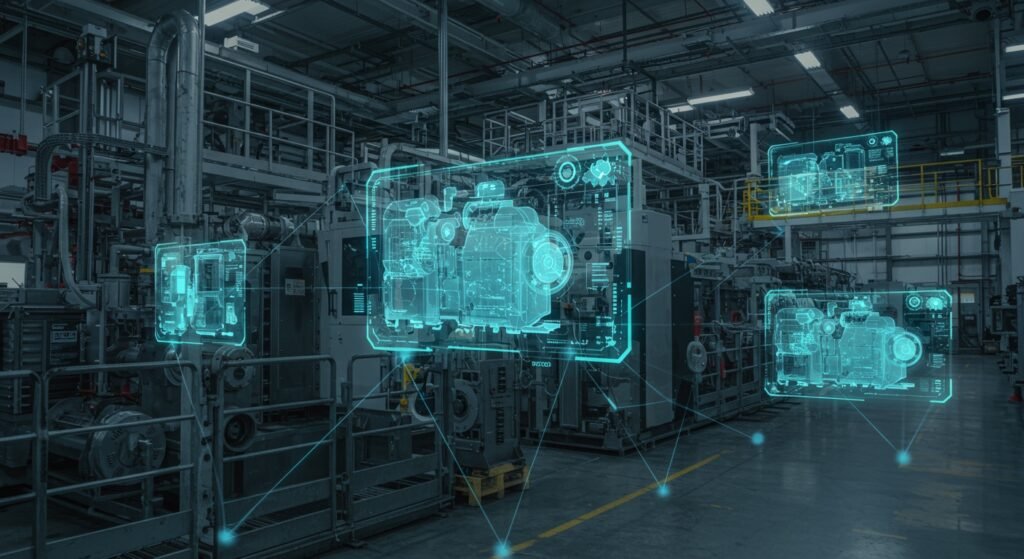
The industrial landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by innovative technologies that promise unprecedented efficiency, safety, and productivity. Among these, Digital Twins in Industrial Systems stand out as a revolutionary concept. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system that serves as a living model, constantly updated with real-time data. This dynamic connection between the physical and digital worlds empowers businesses to monitor, analyze, and optimize operations like never before. From manufacturing plants to energy grids, the application of digital twins is redefining what’s possible in modern industry.
Table of Contents
- What Are Digital Twins?
- How Digital Twins Work
- 7 Revolutionary Benefits of Digital Twins in Industrial Systems
- Key Challenges and Considerations
- The Future of Industrial Engineering
- Conclusion
What Are Digital Twins?
At its core, a digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system, spanning its lifecycle, updated with real-time data, and using simulation, machine learning, and reasoning to help decision-making. Unlike a simple 3D model, a digital twin is dynamic and interconnected. It’s a living model that evolves with its physical counterpart, providing insights into performance, potential issues, and optimization opportunities. These twins are built using vast amounts of data collected from sensors, historical records, and other sources, processed by advanced analytics and AI algorithms.
How Digital Twins Work
The functionality of digital twins relies on a sophisticated interplay of various technologies, creating a seamless bridge between the physical and digital realms. Understanding this mechanism is key to appreciating their transformative power.
Data Collection and Integration
The foundation of any effective digital twin lies in robust data collection. Sensors embedded within physical assets (e.g., machines, turbines, vehicles) continuously gather operational data, including temperature, pressure, vibration, energy consumption, and more. This data is then transmitted to a cloud platform or edge computing system, where it is integrated with historical data, design specifications, and even external factors like weather or market conditions. This holistic data set creates a comprehensive understanding of the physical asset’s state.
Modeling and Simulation
Once data is collected, sophisticated modeling software creates the virtual replica. This involves detailed 3D models, physics-based simulations, and behavioral algorithms that accurately mimic the physical asset’s characteristics and performance. Engineers can then run simulations to test different scenarios, predict outcomes, and identify potential failures before they occur in the real world. This capability is invaluable for design optimization, process improvement, and risk mitigation.
Real-time Monitoring and Analysis
Perhaps the most compelling aspect of digital twins is their real-time monitoring capability. As new data streams in, the digital twin is updated instantaneously, providing an up-to-the-minute view of the physical asset’s condition. Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms process this continuous data flow, identifying anomalies, predicting maintenance needs, and offering insights for operational adjustments. Dashboards and alerts provide operators with actionable information, enabling proactive decision-making.
7 Revolutionary Benefits of Digital Twins in Industrial Systems
The adoption of Digital Twins in Industrial Systems brings a myriad of advantages, revolutionizing how industries operate, innovate, and maintain their assets. These benefits span across the entire product lifecycle and operational workflow.
1. Optimized Operations and Efficiency
Digital twins enable precise monitoring and control of industrial processes, leading to significant improvements in operational efficiency. By continuously analyzing performance data, operators can identify bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and fine-tune machine parameters for maximum output with minimal waste. This level of optimization translates directly into cost savings and increased productivity.
2. Predictive Maintenance and Reliability
One of the most celebrated benefits is the shift from reactive to predictive maintenance. Digital twins can analyze sensor data and historical trends to forecast potential equipment failures before they happen. This allows companies to schedule maintenance proactively during planned downtime, avoiding costly unscheduled repairs and reducing overall downtime. This significantly enhances asset reliability and extends equipment lifespan.
3. Enhanced Design and Prototyping
Before physical production, digital twins allow engineers to virtually design, test, and iterate on products and processes. This reduces the need for expensive physical prototypes, accelerates time-to-market, and allows for thorough performance validation in a simulated environment. Design flaws can be identified and corrected early, saving substantial resources.
4. Improved Risk Management and Safety
By simulating various operational scenarios, including potential failure modes and external stresses, digital twins help assess and mitigate risks. They can model the impact of different operational decisions on safety protocols and environmental compliance, allowing organizations to develop more robust risk management strategies and create safer working environments for personnel.
5. Remote Monitoring and Control
Digital twins facilitate remote monitoring of assets and processes, which is particularly beneficial for geographically dispersed operations or hazardous environments. Operators can gain insights and even control certain aspects of equipment from a central location, enhancing responsiveness and reducing the need for on-site presence, leading to further efficiency gains and reduced travel costs.
6. Supply Chain Optimization
Extending beyond individual assets, digital twins can model entire supply chains. This provides end-to-end visibility, allowing businesses to track goods, predict disruptions, and optimize logistics. By simulating different supply chain configurations, companies can identify the most resilient and cost-effective strategies, improving overall responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
7. Sustainability and Resource Management
Digital twins offer powerful tools for monitoring and optimizing resource consumption, including energy, water, and raw materials. By identifying areas of inefficiency and waste, they help organizations reduce their environmental footprint and achieve sustainability goals. This aligns with global efforts towards greener industrial practices and responsible resource management.
Key Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of digital twins is immense, their implementation is not without challenges. These include the significant initial investment in sensor technology, data infrastructure, and specialized software. Data security and privacy are paramount concerns, given the sensitive nature of operational data. Furthermore, integrating legacy systems with new digital twin platforms can be complex, requiring careful planning and skilled personnel. Addressing these challenges is crucial for successful adoption and realizing the full benefits of this technology.
The Future of Industrial Engineering
The integration of digital twins is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0, paving the way for hyper-connected and intelligent factories. As technologies like AI, IoT, and 5G continue to advance, the capabilities of digital twins will only expand, leading to even more sophisticated simulations and predictive models. These advancements will revolutionize industrial engineering, transforming everything from product design to global supply chain management. The future promises a world where every physical asset has a dynamic digital counterpart, enabling unparalleled levels of insight and control. To dive deeper into how emerging technologies are reshaping the sector, learn more about industrial automation innovations on our blog.
Here’s a comparison highlighting the shift from traditional to digital twin-enabled operations:
| Feature | Traditional Operations | Digital Twin-Enabled Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Manual checks, periodic inspections | Real-time, continuous, remote |
| Maintenance | Reactive (break-fix), time-based | Predictive, prescriptive, proactive |
| Decision Making | Based on historical data, experience | Data-driven, simulation-supported, AI-enhanced |
| Product Development | Physical prototyping, costly iterations | Virtual prototyping, rapid iteration, reduced costs |
| Efficiency | Optimized through trial and error | Continuously optimized via simulation and analytics |
Conclusion
Digital Twins in Industrial Systems represent more than just a technological advancement; they signify a paradigm shift in how industries operate. By creating dynamic, real-time virtual replicas of physical assets and processes, they unlock unprecedented opportunities for optimization, efficiency, and innovation. While challenges exist, the undeniable benefits in productivity, cost savings, and risk mitigation make digital twins an indispensable tool for any forward-thinking industrial enterprise. Embracing this technology is not just about staying competitive; it’s about leading the charge into the next era of industrial excellence. For further reading on the broader context of industrial technological advancements, you might find this resource on Industry 4.0 insightful.